
一种基于多孔聚(乳酸-乙醇酸)共聚物(PLGA)微球的人脐静脉内皮细胞/肝癌细胞共培养模型。
Introduction
思路:
- 二维单层培养不能复现高复杂度的、天然的细胞外基质微环境,如细胞-细胞/细胞-基质相互作用。三维肿瘤模型可以仿生精细的细胞空间排布用于预测抗肿瘤试剂的效率和耐药。
- 三维支架模型相比于二维平台和三维细胞球培养更能反应肿瘤微环境,其中聚合多孔结构在细胞相互作用和ECM重塑中具有优势。
- 归因于内部的孔隙与相互连接的窗口,多孔结构有利于细胞的附着;
- 基于明胶的多孔微支架通过诱导沉积更多的细胞外蛋白,有效地促进了细胞的生长和代谢活动。
- 尽管这些盛行的模型有的已被证明能有效地模仿肿瘤的复杂成分,但仍需要提高基于三维支架微结构的功效和细胞-细胞相互作用。
- 作者先前已经用微流控技术制造了PLGA多孔微粒(PMs)用于细胞传递。
- 将非实质细胞与肿瘤细胞进行共培养可以增强细胞与基质的相互作用,从而调节肿瘤细胞的生长、增殖和转移。
- 在原生肿瘤组织中,细胞可以通过内皮细胞(ECs)的旁分泌作用直接获得肿瘤诱导因子;反之,在肿瘤形成过程中,血管生长因子分泌,以诱导ECs向肿瘤组织发芽,并重建血管进行营养运输。
- 在没有血管网络的情况下,营养供应和代谢物的排泄仅仅依靠物理扩散,这严重限制了肿瘤细胞的生长和迁移。ECs与肿瘤细胞的共培养是建立血管功能的最直接的方法,有助于构建肿瘤组织模型并用于研究肿瘤发生、癌症病理和药物研发。
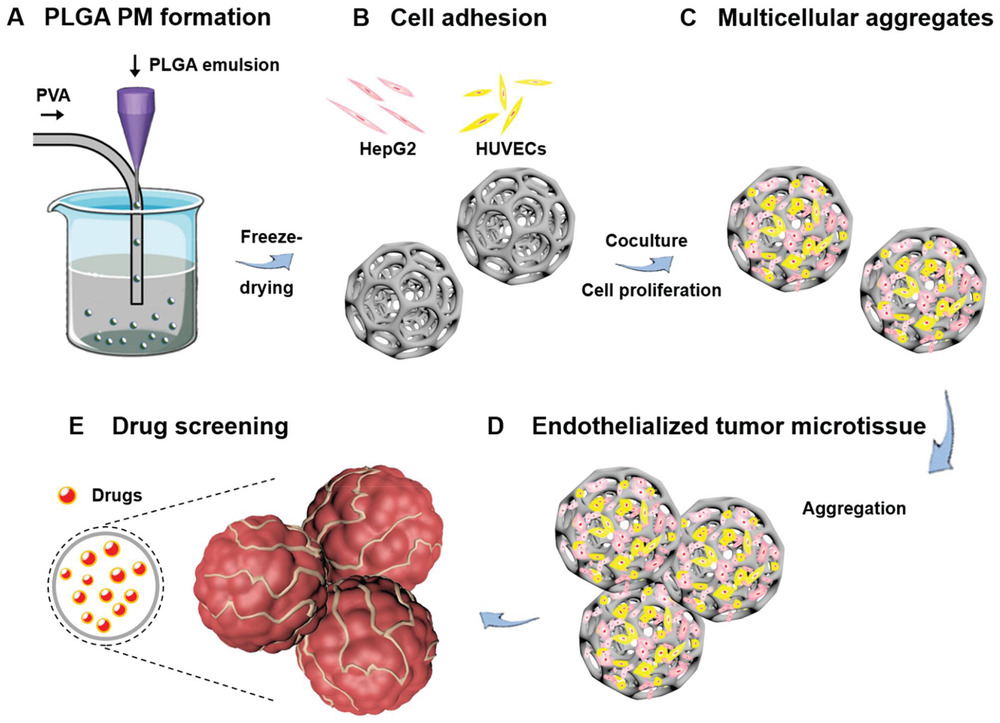
- (A)使用微流控技术生成PLGA PMs。即将明胶水溶液与PLGA的DCM溶液混合作为分散相,PVA水溶液为连续相。
- (B-C)PLGA PMs中HUVEC细胞和HepG2细胞的粘附、增殖导致内皮化多细胞肿瘤聚集体的形成。
- (D)通过单独的多细胞肿瘤聚集体的进一步相互作用构建内皮化肿瘤微组织。
- (E)化疗药物DOX和CIS作为模型药物对内皮化肿瘤微组织进行抗癌药物评估。
Fabrication and Characterizations of PLGA PMs

- (A-C)PLGA PMs的尺寸分布和形态的SEM图像。可以看到制造的球状PMs具有开放、互通的多孔结构。
- (D-E)PLGA PMs的孔径分布和傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)分析。
- (F)通过气相色谱(GC)分析有机溶剂残留物。检测二氯甲烷(DCM)的残留量,通过对照可知,PLGA PMs中无DCM残留。
- (G)体外细胞毒性试验(CCK-8法)显示HepG2细胞在与不同浓度的PLGA PMs(0.25、0.50、1.00和1.50 mg mL-1)以及不同时间(24、48和72 h)处理的存活率均保持在 80% 以上,表明基于PLGAs的微架构与HepG2细胞高度兼容。
Fabrication and Characterizations of Cell-Laden PLGA PMs

- (A)用于培养载有细胞的PLGA PMs的动态培养方法,培养条件为37 °C和110 rpm。
- (B)激光扫描共聚焦显微镜(CLSM)图像显示了在不同时间(6 h和1 d)的动态培养中,用PLGA PMs培养的HepG2细胞的粘附。荧光在最初6 h内主要分布在外围,即HepG2细胞粘附到PLGAs结构的表面。随着时间增加,荧光水平增加,表明细胞密度增加。
- (C)CLSM图像显示3 d后PLGA PMs上HepG2细胞骨架(鬼笔环肽染色)。
- (D)与培养时间相关的单个微球上的HepG2细胞数。培养过程中,每个微球的细胞数量从最初24 h的平均5370个细胞逐渐增加到48 h后的约9100个细胞。
- (E)CLSM图像显示用PLGA PMs动态培养的HUVEC细胞在不同时间(6 h和1 d)的粘附,与HepG2呈现相似趋势。
- (F)与培养时间相关的单个微球上的HUVEC细胞数。
- (G)CLSM图像显示3 d后PLGA PMs上HUVEC细胞的内皮特异性连接蛋白(血管内皮钙黏蛋白,VE-Cad)。
Formation of Tumor Microtissues and Bioefficacy Assessments
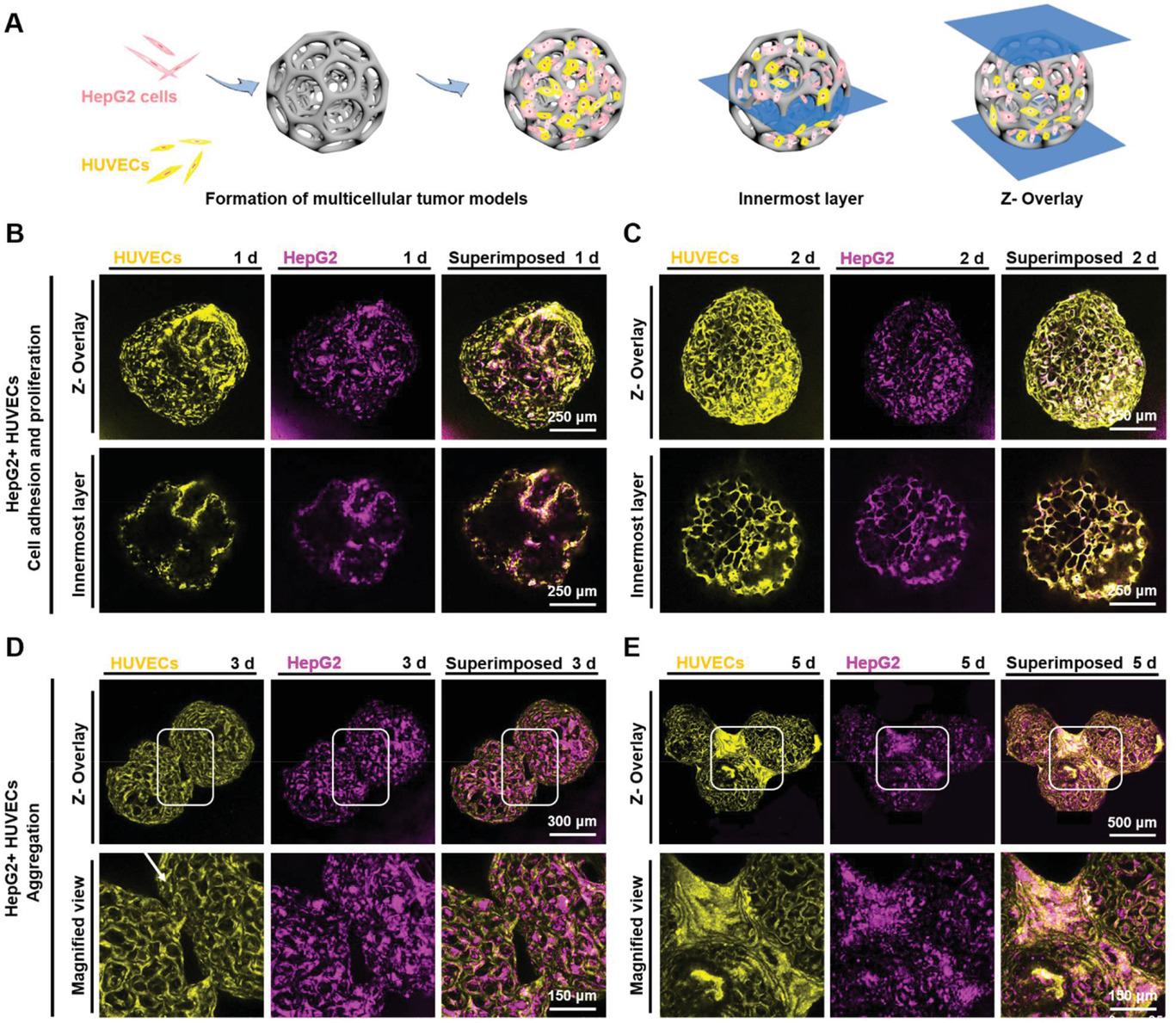
- (A)HepG2细胞和HUVEC细胞共培养的动态培养。
- (B-E)荧光显微图像显示共培养1、2、3和5 d后HepG2细胞(Qtracker 655,紫色)和HUVEC(Qtracker 525,黄色)在PLGA PMs上的粘附和分布。可以看到,实现了多个PLGA PMs的聚合。

- (A)荧光和白光图像显示共培养 3、4、5、7和10 d后,PLGA PMs上HepG2细胞和HUVEC细胞的生长。3 d后观察到载有细胞的PLGA PMs之间的连接(白色方块),并且这些PLGAs结构的聚集是通过延长培养时间来实现的。
- (B)ELISA测量的白蛋白(Alb)的释放水平。由于Alb的粘性和神经胶质特性,增加的Alb分泌可能有助于PLGAs结构的聚集。
- (C)ELISA测量的多药耐药相关蛋白(MRP)释放水平。其参与调节细胞内成分的重新分配以保护细胞。
Drug Screening

- (A-B)细胞在与不同浓度的(A)DOX和(B)CIS孵育后的相对活力。不同细胞类型的活力随着DOX浓度和暴露时间的增加而降低,CIS也观察到相同的趋势。
- (C-D) 荧光显微镜图像显示2D和3D培养细胞在不同时间点(2、4和12 h)的吖啶橙/溴化乙锭(AO/EB)染色。活细胞和死细胞分别被染成绿色和红色,黄色的细胞代表与药物孵育后细胞凋亡的早期阶段。
- (E-F)2D和3D培养的HepG2细胞和HUVEC细胞对(E)DOX和(F)CIS的剂量反应。
Cellular Internalization Efficiency

- (A)2D共培养的HepG2细胞和HUVEC细胞在不同时间点 (2和4 h) 的DOX内化。DOX从2 h开始内化到细胞中,并且在4 h时在细胞中积累了大量的DOX。
- (B)在3D动态培养下,多细胞聚集体(HepG2细胞和HUVEC细胞)中的DOX内化。
- (C-F)荧光显微镜图像显示DOX在不同时间点(2、4 和6 h以及1 d)在多细胞聚集体(HepG2细胞和 HUVEC细胞)中的细胞内化。在与2D培养相同的时间(2 和 4 h)孵育后,在单个微球的外围观察到有限的DOX,而1 d后DOX量逐渐增加。

- (A-B)荧光显微图像显示DOX(红色)在6 h和1 d的细胞内化以及细胞核的DAPI染色(蓝色)。孵育6 h后观察到少量的DOX,红色荧光分布表明DOX主要内化在肿瘤微组织的外围。
- (C)DOX处理1 d时多细胞肿瘤微组织中细胞的凋亡分析(膜联蛋白Annexin染色,绿色:活细胞;红色:死亡和晚期凋亡细胞;黄色:凋亡细胞)。低活力的细胞主要分布在微组织的外围。
Conclusions
- 使用与HUVECs/HepG2细胞共培养的PLGA PMs构建3D肝肿瘤微组织模型,用于药物筛选的潜在应用。
- HUVECs和 HepG2在PLGA PMs内共培养,以促进PLGA PMs的连接和聚集,并在体外形成生理相关的肿瘤微环境。
- 此外,发现在使用DOX和CIS作为模型药物时,与2D培养方法相比,该架构的药物评估能力显著增强。其增强不仅表现在肿瘤微组织模型能够显着延长药物分子内化到内部的时间,还表现在不同部位的细胞对药物的利用度不同。
- 总之,基于PLGA PMs与HUVECs和HepG2细胞共培养的多细胞肝肿瘤微组织模型的构建对于促进体外药物筛选具有潜在的意义,从而为药物开发和癌症治疗提供了一个有利平台。
Reference
Wang Y, Kankala R K, Zhang J, et al. Modeling Endothelialized Hepatic Tumor Microtissues for Drug Screening[J]. Advanced Science, 2020, 7(21): 2002002.



